Javid R. Ibrahimov
Abstract
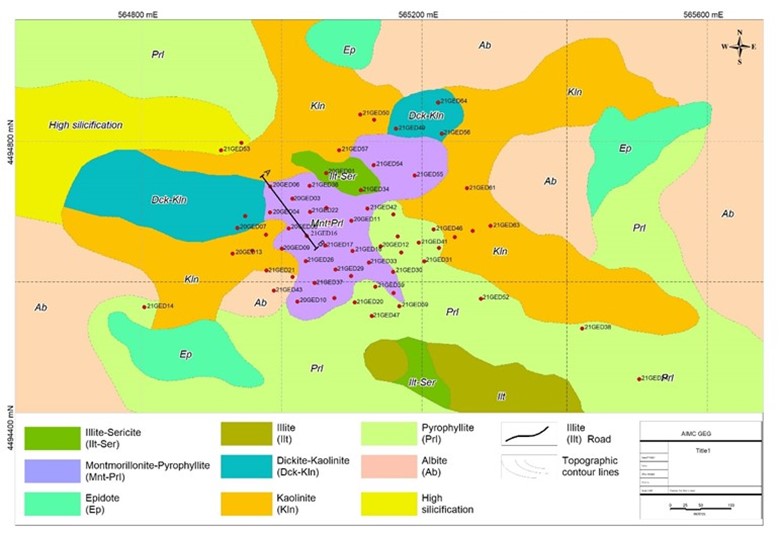
The Zafar copper-gold deposit is located Gadabay ore district, 3.5 km northwest of the Gadabay gold mine and 2.5 km southwest of the Ugur mine. This newly discovered copper-gold deposit contains 6.8 million tonnes of measured resources (0.5% Cu, 0.4 ppm Au, and 0.6 % Zn, according to Zafar JORC Min-eral Resource Estimate Update Report 2022). This study investigates the spatial and mineralogical char-acteristics of hydrothermal alteration zones within the Zafar deposit and evaluates the influence of tec-tonic regime and magmatic activity on their development and distribution. Detailed field observations, petrographic analyses, and geochemical data reveal a well-defined alteration zonation consisting of argil-lic (minerals: pyrophyllite, kaolinite, alunite, diaspore, dickite, quartz), phyllic (minerals: sericite, illite, quartz, pyrite), propylitic (minerals: chlorite, epidote, albite, calcite, actinolite, pyrite) and silification as-semblages, typical of intermediate sulfidation epithermal systems.